Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a federal parliamentary republic in west-central Europe. The country consists of 16 states, and its capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi) and has a largely temperate seasonal climate.

Full name: Federal Republic of Germany
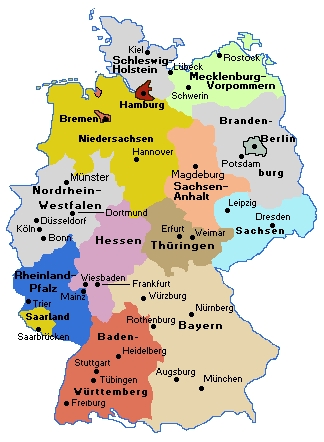
Capital: Berlin
Area: 357.123,50 km2
% Water: 2,18%
Popolulation: 81.772.000
Density: 229/km2
Continent: Europe
Valuta: Euro 
With 81.8 million inhabitants, it is the most populous member state in the European Union. Germany is one of the major political and economic powers of the European continent and a historic leader in many theoretical and technical fields.

A region named Germania, inhabited by several Germanic peoples, was documented before AD 100. During the Migration Period, the Germanic tribes expanded southward and established successor kingdoms throughout much of Europe. Beginning in the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation while southern and western parts remained dominated by Roman Catholic denominations, with the two factions clashing in the Thirty Years’ War, marking the beginning of the Catholic–Protestant divide that has characterized German society ever since. Occupied during the Napoleonic Wars, the rise of Pan-Germanism inside the German Confederation resulted in the unification of most of the German states in 1871 into the German Empire, which was Prussian dominated.
After the German Revolution of 1918–1919 and the subsequent military surrender in World War I, the Empire was replaced by the parliamentary Weimar Republic in 1918, and some of its territory partitioned in the Treaty of Versailles. Despite its lead in many scientific and artistic fields at this time, amidst the Great Depression, the Third Reich was proclaimed in 1933. The latter period was marked by Fascism and World War II. After 1945, Germany was divided by allied occupation, and evolved into two states, East Germany and West Germany. In 1990 the country was reunified.
Germany was a founding member of the European Community in 1957, which became the EU in 1993. It is part of the Schengen Area and since 1999 a member of the euro area. Germany is a great power and member of the United Nations, NATO, the G8, the G20, the OECD and the Council of Europe, and took a non-permanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2011–2012 term.

Germany has the world’s fourth largest economy by nominal GDP and the fifth largest by purchasing power parity. Germany is the second largest exporter and third largest importer of goods. The country has developed a very high standard of living and features a comprehensive system of social security; the country has the world’s oldest universal health care system. Germany has been the home of many influential philosophers, music composers, scientists and inventors, and is known for its cultural and political history.
German reunification and the EU
Based on the Berlin/Bonn Act, adopted on 10 March 1994, Berlin once again became the capital of the reunified Germany, while Bonn obtained the unique status of a Bundesstadt (federal city) retaining some federal ministries. The relocation of the government was completed in 1999. Since reunification, Germany has taken a more active role in the European Union and NATO. Germany sent a peacekeeping force to secure stability in the Balkans and sent a force of German troops to Afghanistan as part of a NATO effort to provide security in that country after the ousting of the Taliban. These deployments were controversial since, after the war, Germany was bound by domestic law only to deploy troops for defence roles. In 2005, Angela Merkel became the first female Chancellor of Germany as the leader of a grand coalition.

Geography
Germany is in Western and Central Europe, with Denmark bordering to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France and Luxembourg to the southwest, and Belgium and the Netherlands to the northwest. It lies mostly between latitudes 47° and 55° N (the tip of Sylt is just north of 55°), and longitudes 5° and 16° E. The territory covers 357,021 km2 (137,847 sq mi), consisting of 349,223 km2 (134,836 sq mi) of land and 7,798 km2 (3,011 sq mi) of water. It is the seventh largest country by area in Europe and the 62nd largest in the world.
Elevation ranges from the mountains of the Alps (highest point: the Zugspitze at 2,962 metres / 9,718 feet) in the south to the shores of the North Sea (Nordsee) in the northwest and the Baltic Sea (Ostsee) in the northeast. The forested uplands of central Germany and the lowlands of northern Germany (lowest point: Wilstermarsch at 3.54 metres / 11.6 feet below sea level) are traversed by such major rivers as the Rhine, Danube and Elbe. Glaciers are found in the Alpine region, but are experiencing deglaciation. Significant natural resources are iron ore, coal, potash, timber, lignite, uranium, copper, natural gas, salt, nickel, arable land and water.

Climate
Most of Germany has a temperate seasonal climate in which humid westerly winds predominate. The climate is moderated by the North Atlantic Drift, the northern extension of the Gulf Stream. This warmer water affects the areas bordering the North Sea; consequently in the northwest and the north the climate is oceanic. Rainfall occurs year-round, especially in the summer. Winters are mild and summers tend to be cool, though temperatures can exceed 30 °C (86 °F).
The east has a more continental climate; winters can be very cold and summers very warm, and long dry periods are frequent. Central and southern Germany are transition regions which vary from moderately oceanic to continental. In addition to the maritime and continental climates that predominate over most of the country, the Alpine regions in the extreme south and, to a lesser degree, some areas of the Central German Uplands have a mountain climate, characterised by lower temperatures and greater precipitation.
Biodiversity
The territory of Germany can be subdivided into two ecoregions: European-Mediterranean montane mixed forests and Northeast-Atlantic shelf marine. As of 2008 the majority of Germany is covered by either arable land (34%) or forest and woodland (30.1%); only 13.4% of the area consists of permanent pastures, 11.8% is covered by settlements and streets.
Plants and animals are those generally common to middle Europe. Beeches, oaks, and other deciduous trees constitute one-third of the forests; conifers are increasing as a result of reforestation. Spruce and fir trees predominate in the upper mountains, while pine and larch are found in sandy soil. There are many species of ferns, flowers, fungi, and mosses. Wild animals include deer, wild boar, mouflon, fox, badger, hare, and small numbers of beavers.
The national parks in Germany include the Wadden Sea National Parks, the Jasmund National Park, the Vorpommern Lagoon Area National Park, the Müritz National Park, the Lower Oder Valley National Park, the Harz National Park, the Saxon Switzerland National Park and the Bavarian Forest National Park. More than 400 registered zoos and animal parks operate in Germany, which is believed to be the largest number in any country. The Zoologische Garten Berlin is the oldest zoo in Germany and presents the most comprehensive collection of species in the world.

Culture
From its roots, culture in German states has been shaped by major intellectual and popular currents in Europe, both religious and secular. Historically Germany has been called Das Land der Dichter und Denker (the land of poets and thinkers). because of its famous writers and a number of noticeable philosophers. The federated states are in charge of the cultural institutions. There are 240 subsidised theatres, hundreds of symphonic orchestras, thousands of museums and over 25,000 libraries spread in Germany. These cultural opportunities are enjoyed by many: there are over 91 million German museum visits every year; annually, 20 million go to theatres and operas; 3.6 million per year listen to the symphonic orchestras. As of 2012 the UNESCO inscribed 37 properties in Germany on the World Heritage List.

Germany has established a high level of gender equality, promotes disability rights, and is legally and socially tolerant towards homosexuals. Gays and lesbians can legally adopt their partner’s biological children, and civil unions have been permitted since 2001. Germany has also changed its attitude towards immigrants; since the mid-1990s, the government and the majority of Germans have begun to acknowledge that controlled immigration should be allowed based on qualification standards. Germany has been named the world’s second most valued nation among 50 countries in 2010. A global opinion poll for the BBC revealed that Germany is recognised for having the most positive influence in the world in 2011.
Cuisine
German cuisine varies from region to region. The southern regions of Bavaria and Swabia, for instance, share a culinary culture with Switzerland and Austria. In all regions, meat is often eaten in sausage form. Organic food has gained a market share of ca. 2%, and is expected to increase further. Although wine is becoming more popular in many parts of Germany, the national alcoholic drink is beer. German beer consumption per person is declining, but at 121.4 litres in 2009 it is still among the highest in the world. The Michelin guide has awarded nine restaurants in Germany three stars, the highest designation, while 15 more received two stars. German restaurants have become the world’s second-most decorated after France.


